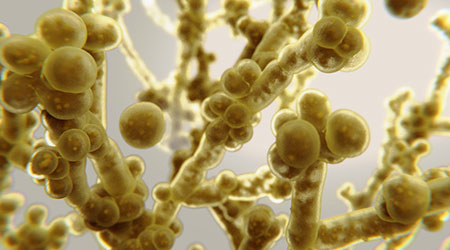
Candida auris can be difficult to get rid of and part of the problem is that hosts shed it via skin cells, according to an article on the Contagion Live website.
Once shed, the pathogen can live for weeks on dry surfaces. It may remain even after surfaces are disinfected.
The risk of contracting C auris is low for most people, even those who reside in traditional nursing homes. Most concerning are the outbreaks at long-term facilities.
As of April 30, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention had identified 654 clinical cases of C auris, primarily in New York City, New Jersey and Chicago.
 Healthcare and Resilience: A Pledge for Change
Healthcare and Resilience: A Pledge for Change Texas Health Resources Announces New Hospital for North McKinney
Texas Health Resources Announces New Hospital for North McKinney Cedar Point Health Falls Victim to Data Breach
Cedar Point Health Falls Victim to Data Breach Fire Protection in Healthcare: Why Active and Passive Systems Must Work as One
Fire Protection in Healthcare: Why Active and Passive Systems Must Work as One Cleveland Clinic Hits Key Milestones for Palm Beach County Expansion
Cleveland Clinic Hits Key Milestones for Palm Beach County Expansion