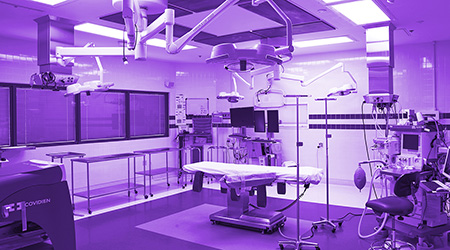
Newly published research shows that light disinfection technology effectively and safely inactivates SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A viruses in a range of real-world clinical settings.
The paper, "The virucidal effects of 405 nm visible light on SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A virus," was published in Scientific Reports on September 30, 2021. It reflects how researchers evaluated the inactivation rate of the SARS-CoV-2 virus using 405 nm visible light under a range of clinical conditions. By applying these findings to a real-world usage model, it is determined that the technology would achieve a SARS-CoV-2 inactivation rate of 94 percent based on 12 hours of occupied room use and 12 hours of unoccupied room use.
The potential of specific wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum is an area of growing clinical interest. Ultraviolet (UV) technologies have demonstrated the ability to reduce virological spread, but potential toxicities have limited its use in occupied spaces. Longer wavelengths with less irradiation energy such as visible light (405 nanometers) have largely been evaluated in bactericidal and fungicidal applications. This research offers some of the strongest evidence to date of the real-world application of 405 nm visible light to inactivate the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A viruses, helping to create safe, occupied spaces.
"Reducing the ability of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A to spread within healthcare settings is paramount," says Adolfo Garcia-Sastre, Ph.D., Director of the Global Health & Emerging Pathogens Institute and Professor of Microbiology and Medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the study's lead investigator. "This research adds important findings to the medical literature. It shows the potential of a simple, non-invasive technological solution to achieve inactivation of these highly disruptive viruses and warrants further evaluation across a range of additional clinical settings to further validate its effectiveness and safety."
The research was published from a partnership between Kenall and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
 Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris
Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens
Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach
Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach The High Cost of Healthcare Violence
The High Cost of Healthcare Violence EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments
EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments