A study has demonstrated an association between antimicrobial resistance and climate change, according to an article on the Earth.com website.
Antimicrobial resistance was first linked to climate change when researchers noticed that resistance increased as temperatures warmed in the U.S.
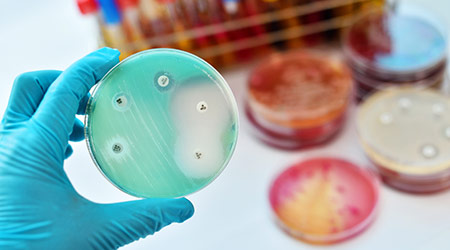
The study looked at 30 countries across Europe and found a widespread, six-year-long presence of carbapenem resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CRPA), Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP), multiresistant Escherichia coli (MREC), and Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
The then looked at the correlation between AMR and seasonal temperatures in each region, considering potential healthcare and socioeconomic factors.
 Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris
Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens
Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach
Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach The High Cost of Healthcare Violence
The High Cost of Healthcare Violence EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments
EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments