The outside temperature can influence the indoor temperature in climate-controlled health care units. That in turn may impact multidrug-resistant organisms (MRDOs), according to an article on the Healio website.
A study in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, found a negative association between humidity and overall MDROs and gram-negative pathogens in units without climate control, and a positive association between temperature and overall MDROs, overall gram-positive pathogens, VRE and P. aeruginosa in the climate-controlled ICU.
Researchers found that temperature did not have a detectable impact on the incidence of MDROs in the non-climate-controlled wards.
For both the ICU and the non-climate-controlled wards, the study found that the inside temperature was significantly correlated with the temperature measured at a nearby meteorological station, indicating that weather conditions outside influenced indoor temperatures.
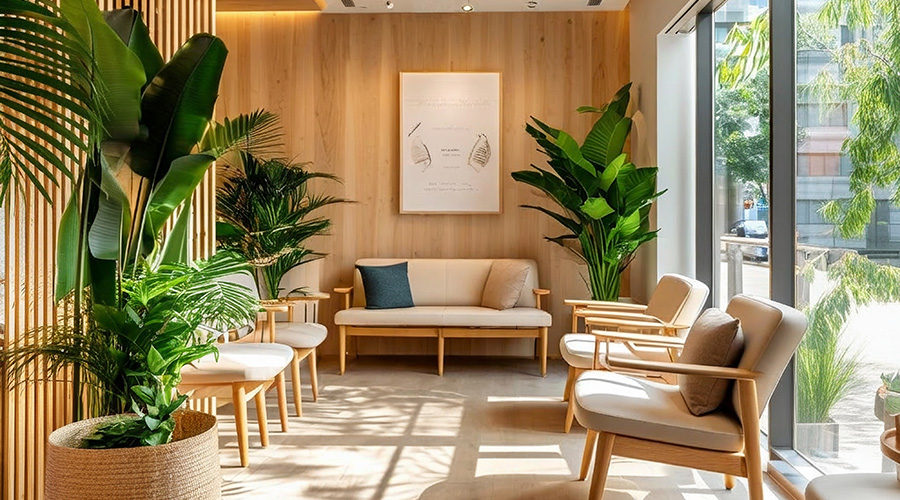
 Grounding Healthcare Spaces in Hospitality Principles
Grounding Healthcare Spaces in Hospitality Principles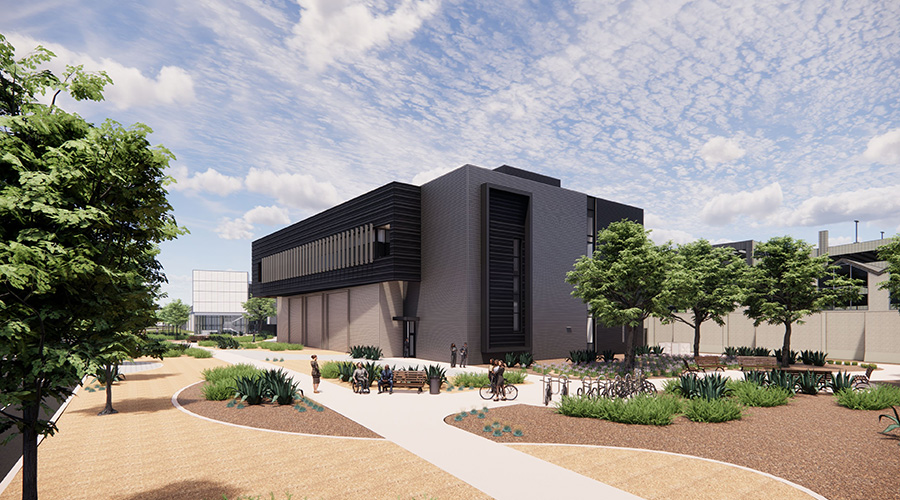 UC Davis Health Selects Rudolph and Sletten for Central Utility Plant Expansion
UC Davis Health Selects Rudolph and Sletten for Central Utility Plant Expansion Cape Cod Healthcare Opens Upper 2 Floors of Edwin Barbey Patient Care Pavilion
Cape Cod Healthcare Opens Upper 2 Floors of Edwin Barbey Patient Care Pavilion Building Sustainable Healthcare for an Aging Population
Building Sustainable Healthcare for an Aging Population Froedtert ThedaCare Announces Opening of ThedaCare Medical Center-Oshkosh
Froedtert ThedaCare Announces Opening of ThedaCare Medical Center-Oshkosh