Candida auris can remain on people's skin and objects, such as hospital furniture and equipment for a long time, according to an article on the Forbes website.
It can be resistant to the three major classes of anti-fungal drugs and it is continuing to spread in hospitals around the world. In act, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has dubbed a "global emerging threat."
There are steps that healthcare facilities can take to control the spread of C. auris. It is key for healthcare facilities with C. auris to regularly and thoroughly clean and disinfect affected patients' rooms with special cleaners (The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has a list) known to work against fungi.
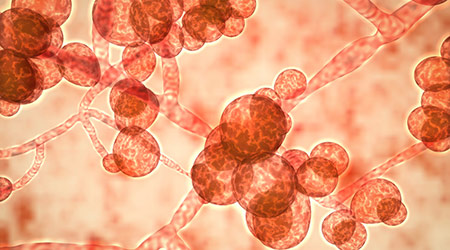
 Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris
Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens
Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach
Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach The High Cost of Healthcare Violence
The High Cost of Healthcare Violence EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments
EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments