Candida auris can be difficult to get rid of and part of the problem is that hosts shed it via skin cells, according to an article on the Contagion Live website.
Once shed, the pathogen can live for weeks on dry surfaces. It may remain even after surfaces are disinfected.
The risk of contracting C auris is low for most people, even those who reside in traditional nursing homes. Most concerning are the outbreaks at long-term facilities.
As of April 30, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention had identified 654 clinical cases of C auris, primarily in New York City, New Jersey and Chicago.
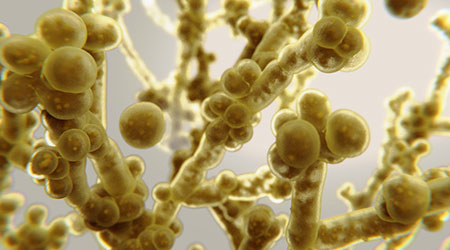
 Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris
Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens
Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach
Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach The High Cost of Healthcare Violence
The High Cost of Healthcare Violence EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments
EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments