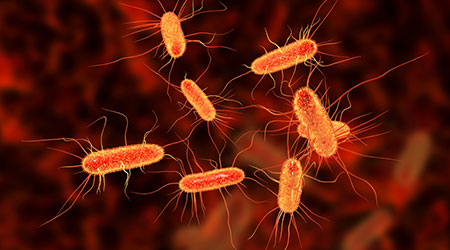
People failing to wash their hands after going to the toilet is behind much of the spread of according to new research.
Scientists have discovered that the likeliest route of transmission for ESBL-E. coli is directly from human to human, with fecal particles from one person reaching the mouth of another, according to an article on the Channel 3000 website.
E.coli is the most common cause of blood poisoning, with more than 40,000 cases per year in England, the article said.
Researchers analyzed 20,000 fecal samples and hundreds of blood samples, publishing their findings in The Lancet Infectious Diseases journal.
 The High Cost of Healthcare Violence
The High Cost of Healthcare Violence EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments
EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments East Tennessee Children's Hospital to Become Dolly Parton Children's Hospital
East Tennessee Children's Hospital to Become Dolly Parton Children's Hospital The Future of the Global Hospital Hygiene Market
The Future of the Global Hospital Hygiene Market Rethinking Fire Safety Inspections
Rethinking Fire Safety Inspections